Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law is a foundational principle in the field of electronics, stating the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. It is succinctly expressed as [@eq:ohms_law]:
\(I = \frac{R}{V} ,\){#eq:ohms_law}
where:
- I is the current flowing through the circuit (in amperes), and
- V is the voltage across the circuit (in volts),
- R is the resistance (in ohms).
Practical Example in Robotics:
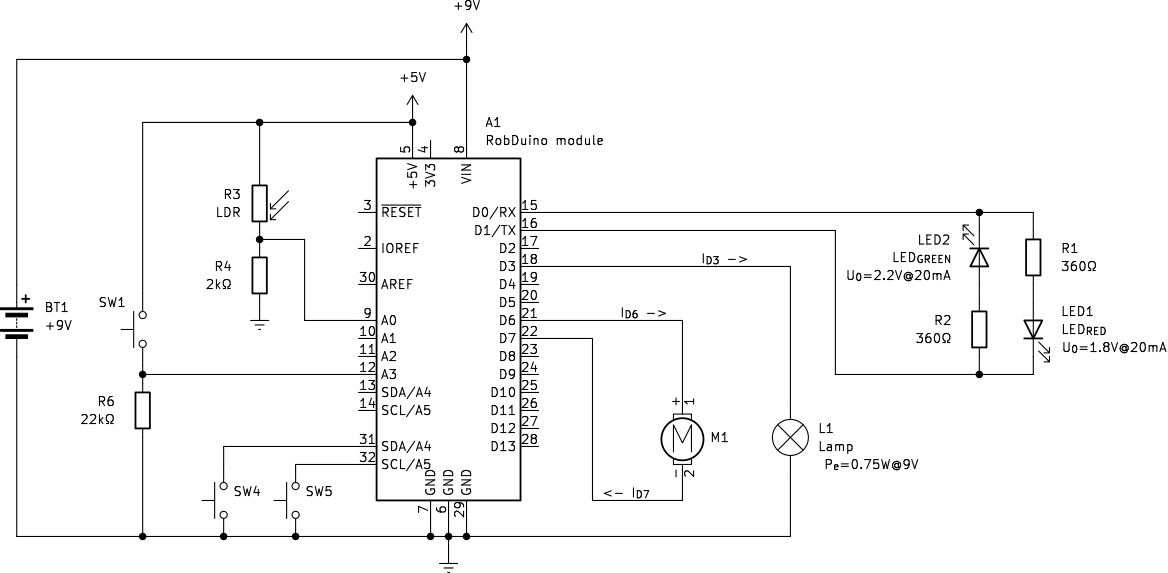 {#fig:RobDuino_Basics_Electronics}
{#fig:RobDuino_Basics_Electronics}
- Consider a simple robotic arm that uses a DC motor for movement ([@fig:RobDuino_Basics_Electronics]). If the motor has a resistance of $20 \Omega$ and is connected to a 9V power supply, Ohm’s Law can determine the current flowing through the motor:
\(I_{motor} = \frac{9V}{10\Omega} = 450 mA .\){#eq:i_mot_cal}
Understanding this helps in selecting the right power source and ensuring that the motor and control electronics are compatible, preventing overheating and damage.
- To apply Ohm’s Law in calculating the current flowing through a light lamp with a power rating of 0.75W at a supply voltage of 9V, and connected to a digital output (D3), we start by understanding the relationship between power, voltage, and current. Ohm’s Law is traditionally stated as [@eq:ohms_law], but we can also express electrical power (Pe) in terms of voltage and current as [@eq:electrical_power]:
\(P_e = V I .\){#eq:electrical_power}
Since we are again interested in electrical current trough lamp we can fill in the data:
\(I_{D3} = \frac{P_e}{V} = \frac{0.75W}{9V} = 83 mA .\){#eq:povwer_d3}
Questions
- Calculate electrical current trough resistor $R_1$ if the voltage across it is $U_{R_1}=7.2V$!
- Calculate the current trough resistor $R_4$ if measured voltage potential on $A_0$ pin is $V_{A_0} = 2V$!